Higher Order Array Methods
Deep dive into the most frequently used array functions like map(), filter() and reduce() methods and their implementation.
Table of contents
Introduction
We have always been using the traditional for-loop for all array-based operations and it has not been worth writing lines of code even just for small operations. It is quite tiresome sometimes. Well, if you are here that means you have the basic idea of why we need these array methods. Let's not waste much time and dive right into it.
The Map Method
The map method iterates over all the elements of the given array, performs the operation on it and returns an array.
The syntax of the
map ()method ismap(callbackFn) map((element, index, array) => { /* ... */ } ) // returns a new array with results of callbackFnParameters are:
callbackFn: Function to execute on each element ofarr. Each time thecallbackFnexecutes, the return value is added to thenewArray.
It accepts one to three argumentselement: The current element being processed in the array.index(optional): The index ofelementsin the array.array(optional): The array on whichmap ()was called upon.
Return Type:- The
map ()method returns a new Array with each element being the result of the callback function. This means that the size of the input array is equal to the size of the resulting array.Best use-case:- When an operation (result) is necessary for every element in an array, it should be used. This is the reason that the resultant array also has the same size as the input array.
NOTE:- The original array or the input array remains immutable. The array which is returned post-mapping has a different memory location.
Example 1:- For a given array, return the square of all its elements.
const arr = [3,5,7,9,11,13]; //input array const calcSquare = inputArr => inputArr.map((arr) => arr*arr); //callback function squaring the element and returning the result const squaredArray = calcSquare(arr); console.log(squaredArray); //[9, 25, 49, 81, 121, 169]In the above example, we made use of the 'map()' method because we needed the result for all the elements of the input array. The step-by-step process is explained
The input array
arris given for which we need to operate on:squaredArrayvariable is declared which is calling thecalcSquarefunction with the input array,arras the argument.The
calcSquarefunction is defined andmap ()method is called on the input array. Since themap ()method is called, the following things take place:the return type will be that of an array
the callback function will act on all the elements of the array and the results will be pushed into
squaredArrayone-by-one.
Once the
map ()method is done with the whole array, the result is printed. Here is the screenshot of the above program
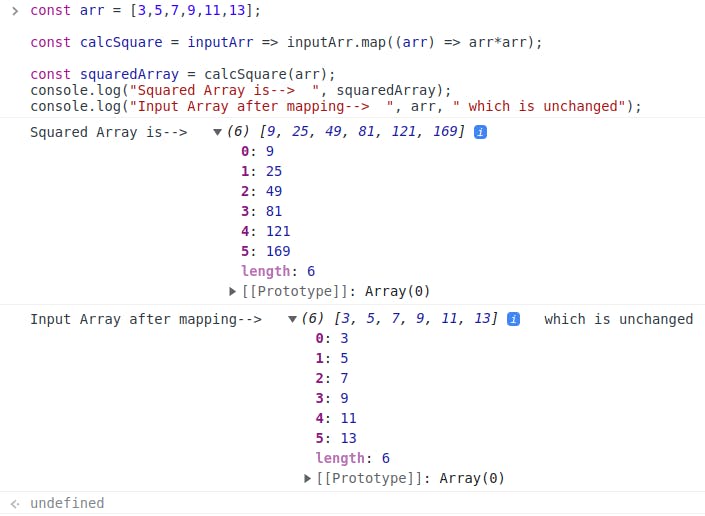
We can see that
the return type is that of an array and the size is 6, which is the same size as the input given.
results are stored sequentially based on the element mapped(
3and9are at the first index of their respective arrays, similarly,5is at the second index and its square,25is also in the second position. )the input array remains unchanged throughout the program.
Example 2:- For a given array of objects of artists, return the name of all the artists.
const artists=[
{name: "Kanye West",
genre: "Hip-Hop & Rap",
grammys: 21
},
{
name: "Whitney Houston",
genre: "R&B, Dance-pop, Soul",
grammys: 6
},
{
name: "The Beatles",
genre: "Psychedelic Rock and Blues",
grammys: 4
},
{
name: "Taylor Swift",
genre: "Pop, Dance, Country",
grammys: 12
},
{
name: "Daft Punk",
genre: "Electronic, Dance",
grammys: 6
},
]
const getName = artistsInput => artistsInput.map((artist) => artist.name);
console.log(getName(artists)); //['Kanye West', 'Whitney Houston', 'The Beatles', 'Taylor Swift', 'Daft Punk']
The process here is the same as the previous example:-
We made use of
map ()method because we had to extract thenameproperty of all the objects in the array.the function
getNameis taking the array of objects as the input and themap ()method is called on the input.The callback function is iterating over the objects and extracts the
namefrom each object.After mapping all the elements, it is returning the resultant array to the
console.logand the array is printed. Below is the screenshot of the program.

The names in the array are in the order in which they are extracted, the result type is that of an array and the size is also the same as that of the input.
The Filter method
Just as the name suggests, this method is used to filter elements from the array.
The filter() method filters out the array's contents to only the elements that pass the test provided in the callback function.
The syntax of
filter ()method isfilter((element) => { /* … */ }) filter((element, index) => { /* … */ }) filter((element, index, array) => { /* … */ })The Parameters are:
callbackFnA function to execute for each element in the array. It should return a value either satisfying or failing the condition.
The function is called with the following arguments:
elementThe current element of the array
indexThe index of the current element being processed in the array.
arrayThe array on which the
filter()method was called upon.
Return Type:- The
filter ()method returns a new Array containing the elements that satisfy the condition in a callback function. This means that the size of the resulting array will always be equal to or smaller than the size of the resulting array.Best use-case:- When the specific elements fulfil the requirements from an array, this method comes in handy.
NOTE:- The original array or the input array remains immutable. The array which is returned post-filter has a different memory location.
Example 1:- For a given array, find the even elements of the array.
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]; //input array const findEven = inputArr => inputArr.filter((arr) => arr%2 ===0); //callback function finding even element const evenElements = findEven(arr); console.log("Even elements are--> ", evenElements); //Even elements are--> [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12]The working is as follows:
The input array,
arris passed as the argument for the functionfindEventhe result will be stored inevenElementsvariable.The
filter ()is iterating over the elements ofarrand the callback function is checking each element with the conditionarr%2 ===0, which is a test to find out even numbers.The numbers that are giving the remainder
0are being filtered out, this means that a copy is being returned and the input array remains intact.The elements that satisfy the condition are printed. Below is the screenshot of the program
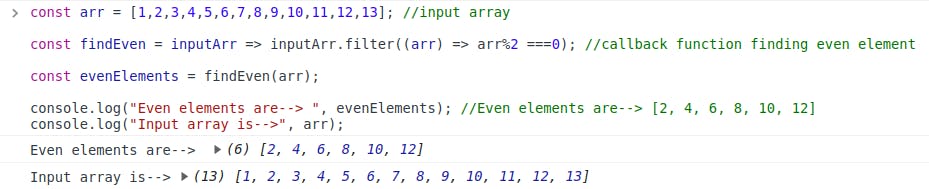
The even elements from the array are being filtered(a copy is returned) and the original array is unchanged.
Example 2:- For a given array of objects of artists, find the name of all the artists with the least number of grammy wins.
const artists=[ {name: "Kanye West", genre: "Hip-Hop & Rap", grammys: 21 }, { name: "Whitney Houston", genre: "R&B, Dance-pop, Soul", grammys: 6 }, { name: "The Beatles", genre: "Psychedelic Rock and Blues", grammys: 4 }, { name: "Taylor Swift", genre: "Pop, Dance, Country", grammys: 12 }, { name: "Daft Punk", genre: "Electronic, Dance", grammys: 6 }, ] const leastGrammy = artistsInput => artistsInput.reduce((max, curr) => max.grammys > curr.grammys ? curr : max)?.name; console.log(leastGrammy(artists)); //['Kanye West','Taylor Swift']This method is quite advanced level due to the usage of 2 methods here,
filter ()andmap ().This is just the extension of thefilter ()method and this is how the execution goes:As usual, our input array
artistsis being passed as an argument for our functionmoreThan10whose job is to find and return the names of the artist who have won more than 10 Grammys.The
filter ()method is being called upon the input array containing objects and all the objects are being filtered out where the value of the propertygrammysis greater than 10.Now, things get difficult due to the usage of
map ()method also so, let's break it down and see what the output would have been without themap()method.Without map()
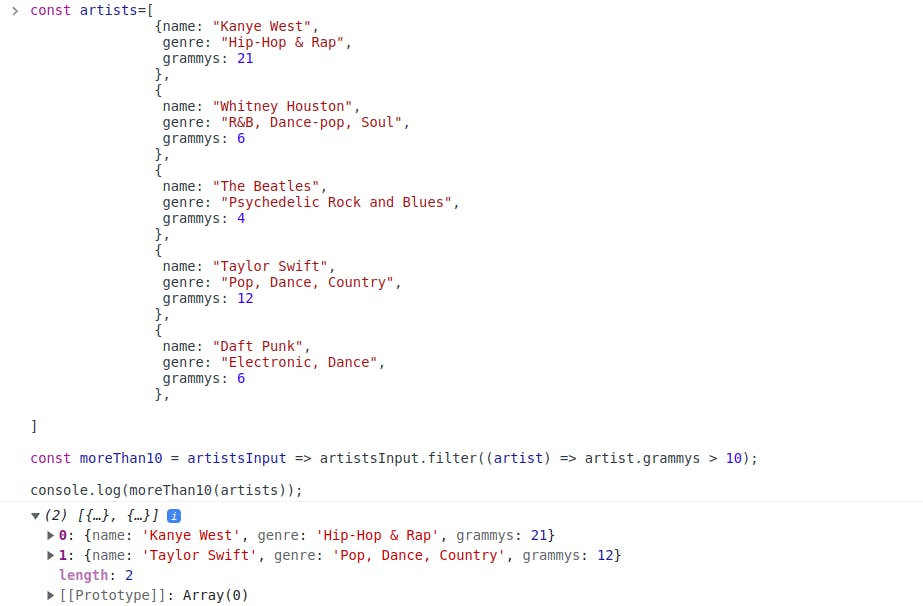
We have received an array which has 2 objects where the value of grammys property is more than 10. Now, we have to extract the name of these artists and recall what we did in the map () example. Yes! we used the map () method to extract a particular property from all the objects of the array. Since here we have received 2 objects, but we want the property name of these objects. Hence, we have to use the map () method. The result is this
With map()
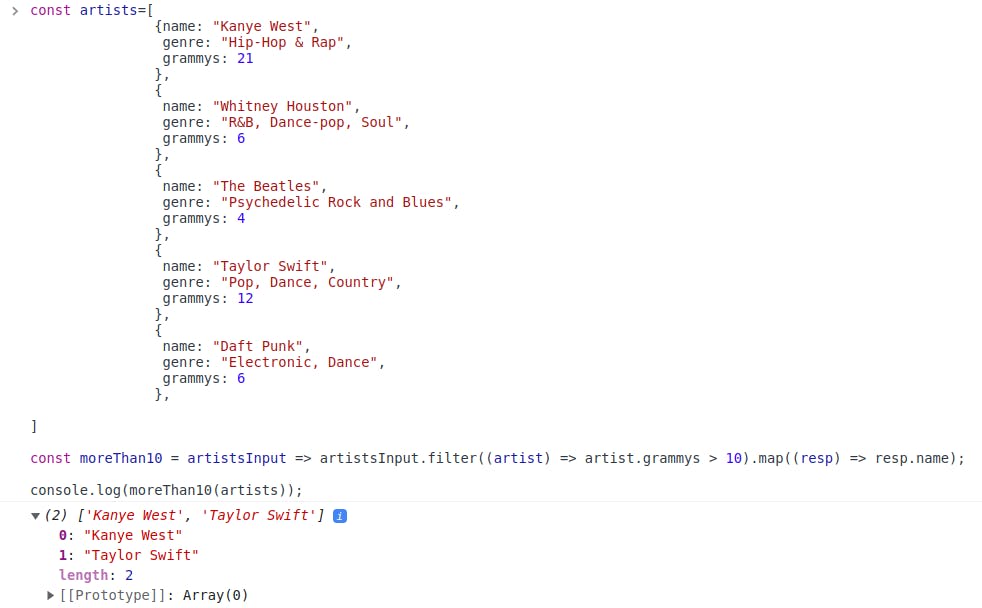
Eureka!!!! We have successfully extracted the name of the artists. This method of using more than 1 method is known as 'chaining of array methods'.
- The original array is intact and the resultant array is very smaller compared to the input array size.
The Reduce Method
This is the most crucial method of all. The main goal of the reduction method is to reduce or lessen the given array into a single value or smaller chunk based on the callback function condition.
The syntax of
reduce ()is:
reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => { /* … */ })
reduce((accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex) => { /* … */ })
reduce((accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array) => { /* … */ }, initialValue) //initialValue is optional
The Parameters are:
callbackFn:A function to execute for each element in the array. Its return value becomes the value of theaccumulatorparameter on the next invocation ofcallbackFn. For the last invocation, the return value becomes the return value ofreduce(): The function is called with the following arguments:accumulator: The value resulting from the previous call tocallbackFn.currentValue: The value of the current element.currentIndex: The index position ofcurrentValuein the array.array: The arrayreduce()was called upon for execution.initialValue: It is optional to initialize it and depends on the requirements. There are 2 scenarios based on the initializationinitialized: the initial value of the
accumulatorwill be the initialized value and the execution will start with the initialized value.not initialized: If not initialized, the starting value of the
accumulatorwill be taken as the value of the first element of the input array.
Return Type:- The
reduce ()method returns a single value.Best use-case:- When there is a need for multiple array methods or conditions that need to be satisfied.
NOTE:- The original array or the input array remains immutable. The array which is returned post-filter has a different memory location.
Example 1:- For a given array, find the sum of all the elements of the array which are at odd indexes.
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]; const oddIndexSum = inputArr => inputArr.reduce((acc,curr,index) => (index %2 !== 0 ) ? acc + curr : acc, 0); const finalSum = oddIndexSum(arr); console.log("Sum of elements at odd indexes is: ", finalSum); //Sum of elements at odd indexes is: 56
The execution is as follows:-
The input array
arris passed as an argument to the functionoddIndexSum, whose purpose is to return the sum of all the values that are present at odd indexes.The
reduce ()method is called on the input array and the initialization starts as follows:-callback functionis initialized with three parameters, acc, curr and index.the variable
accis responsible to store the sum of the values that are at odd indices. It is 0 since we have provided the initial value in the callback function.curris the value of the current variable. In the beginning, the value of curr is curr [0], i.e. 1indexvariable is the value of the index of the current variable.
The value of the index is checked and the ternary operator is used for the sum. If the index is at odd index, the value of the current element,
curris added toaccand its value is returned for the next callback.If the index is at an even position, the
accis returned for the next callback and the even index values are rejected.When all the elements are iterated, the
accis returned. After the execution, the result is as follows:-
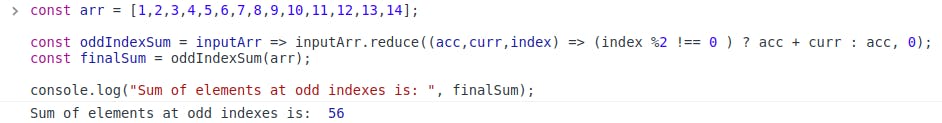
This acc variable is used to store the sum and is returned. The returned value is stored in finalSum and hence the value we get is 56.
Example 2:- For a given array of objects of artists, find the name of all the artist that has the least number of grammys.
const artists=[ {name: "Kanye West", genre: "Hip-Hop & Rap", grammys: 21 }, { name: "Whitney Houston", genre: "R&B, Dance-pop, Soul", grammys: 6 }, { name: "The Beatles", genre: "Psychedelic Rock and Blues", grammys: 4 }, { name: "Taylor Swift", genre: "Pop, Dance, Country", grammys: 12 }, { name: "Daft Punk", genre: "Electronic, Dance", grammys: 6 }, ] const leastGrammy = artistsInput => artistsInput.reduce((min, curr) => min.grammys > curr.grammys ? curr : min)?.name; const minGrammys = leastGrammy(artists); console.log("Artist with the least grammy is: ", minGrammys ) //['The Beatles']The working of the above code is as follows:-
The input array is passed to the
leastGrammyfunction for finding the name with the least number of grammysThe
reduce ()method is called on the object and the initialization takes place. The initial value is not given because we are taking the first value as the minimum value.Now, the value of the current object and minimum object are being compared, if the current one is smaller, its value is pushed into
minvariable and this becomes the smallest till now.This process goes on until the smallest object is not found. Once the smallest value is found, the
nameproperty is returned usingoptional chaining (?.)The
nameproperty of the returned object is printed as the result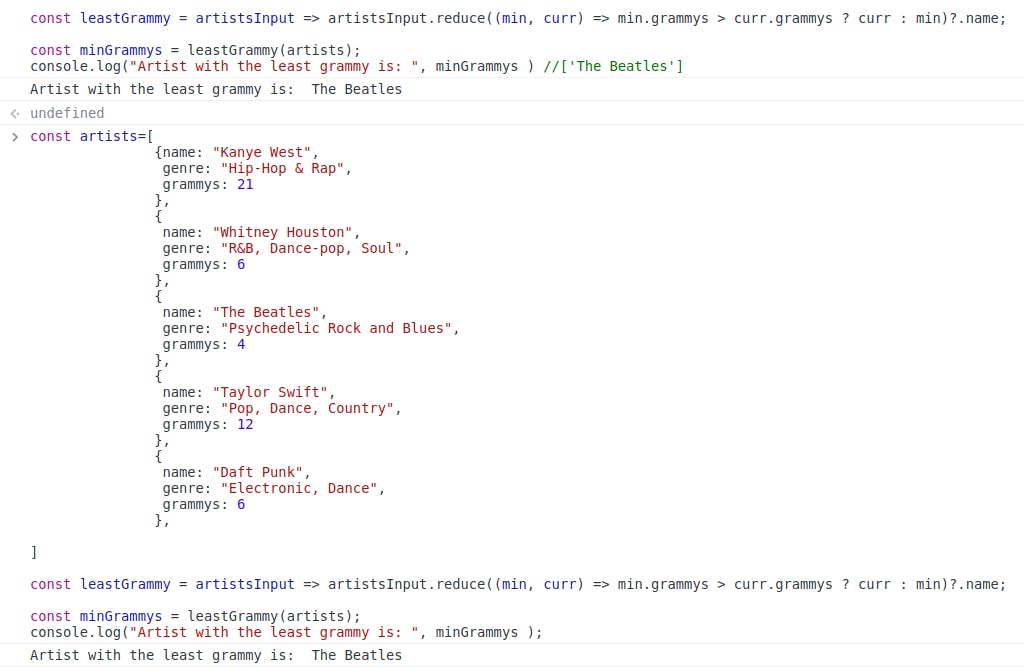
As you can see the name of the artist has been printed who has the least number of grammys in the array. The object is extracted first, and then the name is extracted further.
I hope this blog would have enabled you to understand these array methods in more detail. Keep practising and implementing the ideas. If you have anything interesting or opportunity, connect with me on LinkedIn or Twitter.
